Need help deciding between Viagra and Cialis? Consider your lifestyle and preferences. Viagra acts faster, providing relief within 30-60 minutes, ideal for spontaneous intimacy. Its effects typically last for four hours.
Cialis, conversely, boasts a longer duration–up to 36 hours–making it a better choice for those seeking more flexible timing. This “weekend pill” allows for intimacy whenever the opportunity arises within that timeframe. However, Cialis’ onset is slower, taking effect in 30 minutes to 2 hours.
Dosage varies for both medications; consult your doctor to determine the appropriate amount based on your individual health profile and needs. Remember, always discuss potential side effects with your physician before starting either treatment. They can guide you toward the best option for your specific circumstances.
- Viagra vs. Cialis: A Detailed Comparison
- Dosage and Side Effects
- Cost Considerations
- Other Factors
- Understanding Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Physical Causes of ED
- Psychological Causes of ED
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Viagra (Sildenafil): Mechanism of Action and Dosage
- Cialis (Tadalafil): Mechanism of Action and Dosage
- Dosage Information
- Possible Dosage Variations
- Comparing Viagra and Cialis: Duration of Effect and Onset
- Onset of Action
- Duration of Effect
- Side Effects and Potential Drug Interactions
- Which Drug is Right for You? Factors to Consider
- Duration of Effect
- Side Effects
- Other Medications
- Cost
- Specific Health Conditions
- Personal Preference
- Dosage Adjustments
- Cost Comparison and Accessibility
- Factors Affecting Cost
- Accessing Medication
- Generic vs. Brand-Name
- Additional Considerations
- Seeking Professional Medical Advice for ED
- Understanding Your Medical History
- Diagnostic Tests
- Treatment Options
- Choosing the Right Approach
- Finding a Specialist
- Maintaining Open Communication
Viagra vs. Cialis: A Detailed Comparison
Choose Viagra if you need a medication that acts quickly, typically within 30-60 minutes, and whose effects last for 4-5 hours. This makes it ideal for spontaneous intimacy.
Select Cialis if a longer duration of action is preferable. Cialis’s effects can last up to 36 hours, allowing for more flexibility in timing. Consider this option if predictability is a priority.
Dosage and Side Effects
Both medications come in various dosages, adjusted based on individual needs and response. Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and indigestion. Rarely, more serious side effects may occur. Always consult your doctor before starting either medication and report any adverse reactions immediately.
Cost Considerations
The cost of Viagra and Cialis can vary depending on your insurance coverage and pharmacy. Generic versions are often more affordable. Discuss pricing with your pharmacist to find the best option for your budget.
Other Factors
Viagra requires sexual stimulation to work; Cialis may lead to spontaneous erections. Individual responses to both medications differ; what works well for one person may not be ideal for another. Your doctor can guide you in making the best choice for your specific circumstances.
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Seek medical advice if you experience persistent difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual intercourse. This is the first step towards diagnosis and treatment. Several factors contribute to ED, including physical and psychological issues.
Physical Causes of ED
Underlying health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and high cholesterol frequently impact blood flow, crucial for erections. Obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption also significantly increase your risk. Nerve damage from injuries or surgery can also disrupt erectile function. Certain medications, including some antidepressants and antihypertensives, have ED as a potential side effect. Hormonal imbalances, particularly low testosterone, are another potential contributor.
Psychological Causes of ED
Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems frequently affect sexual performance. Performance anxiety, the fear of failing to perform sexually, can create a vicious cycle. Addressing these underlying psychological issues is essential for successful treatment. Therapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can be highly effective in managing these factors.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Your doctor will conduct a thorough medical history review and physical examination. Blood tests may check testosterone levels and rule out other health problems. Lifestyle modifications, such as weight management, exercise, smoking cessation, and moderate alcohol consumption, often improve symptoms. Oral medications like Viagra and Cialis are commonly prescribed, but other treatment options, including injections, vacuum erection devices, and surgery, are available. The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s health, preferences, and the underlying cause of ED.
Viagra (Sildenafil): Mechanism of Action and Dosage
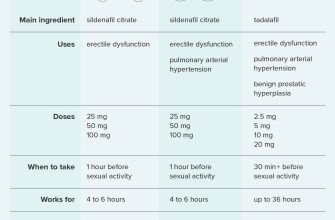
Sildenafil, the active ingredient in Viagra, works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), an enzyme that breaks down cyclic GMP. Increased cyclic GMP levels relax the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, allowing increased blood flow and facilitating an erection.
The recommended starting dose of Viagra is 50 mg taken orally, approximately one hour before sexual activity. This dose may be adjusted based on individual response and tolerance, with a maximum recommended dose of 100 mg per day. Never exceed the recommended dose.
Some men find a lower dose (25 mg) sufficient, while others may require the higher dose. Your doctor will help you determine the appropriate dosage for your needs.
| Dosage | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | As needed, up to once per day | May be sufficient for some individuals |
| 50 mg | As needed, up to once per day | Common starting dose |
| 100 mg | As needed, up to once per day | Maximum recommended dose |
Viagra’s effects typically last for 4-5 hours. Factors like age, overall health, and other medications can influence both effectiveness and duration. Consult your physician before using Viagra, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. They can assess your suitability for the drug and advise on potential interactions.
Cialis (Tadalafil): Mechanism of Action and Dosage
Cialis works by increasing blood flow to the penis. This happens because Tadalafil, the active ingredient, inhibits a specific enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). PDE5 normally breaks down a compound called cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which is crucial for achieving and maintaining an erection. By blocking PDE5, Cialis allows cGMP levels to remain high, resulting in relaxed blood vessels and increased blood flow.
Dosage Information
The recommended starting dose of Cialis is 10mg, taken as needed, at least 30 minutes before sexual activity. The effect can last up to 36 hours.
- Your doctor may adjust your dose based on your response and individual needs. Never adjust the dosage yourself without consulting your doctor.
- Maximum daily dose is 20mg. Exceeding this dose doesn’t increase effectiveness and may increase the risk of side effects.
Possible Dosage Variations
In certain cases, your doctor might prescribe a different dosage regimen:
- Daily use: A low dose (2.5mg or 5mg) can be taken daily to maintain readiness for sexual activity.
- Higher doses (up to 20mg): May be prescribed for those who don’t respond well to lower doses, but only under careful medical supervision.
Remember to discuss any health concerns or medications you are taking with your doctor before starting Cialis. This information is for educational purposes only and should not substitute advice from a qualified healthcare professional.
Comparing Viagra and Cialis: Duration of Effect and Onset
Viagra typically takes 30-60 minutes to become effective, with effects lasting roughly 4-5 hours. Cialis, on the other hand, can start working within 30 minutes, but its effects can persist for up to 36 hours, earning it the nickname “the weekend pill”. This significant difference in duration is due to the varying half-lives of the active ingredients, sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis).
Onset of Action
While both medications aim for similar results, their onset times vary. Consider the timing of planned intimacy when choosing between the two. If spontaneity is desired, Cialis’s longer duration and potentially quicker onset could be advantageous. For those seeking a more predictable timeframe, Viagra’s shorter duration and relatively faster onset might be preferred.
Duration of Effect
The extended duration of Cialis offers significant flexibility. It allows for sexual activity at different points within the 36-hour window, making it convenient for couples with unpredictable schedules. Viagra’s shorter duration requires more precise timing, making it best suited for situations where intimacy is planned well in advance.
Side Effects and Potential Drug Interactions
Always discuss potential side effects and interactions with your doctor before starting Viagra or Cialis. Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. Less common, but serious, side effects include sudden vision loss or hearing loss; seek immediate medical attention if these occur.
Certain medications can interact negatively with Viagra and Cialis. These include nitrates (used to treat chest pain), alpha-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure and enlarged prostate), and some antifungals. The combination can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
Here’s a table summarizing some key interactions:
| Medication Type | Potential Interaction | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrates (e.g., nitroglycerin) | Severe drop in blood pressure | Do not take Viagra or Cialis with nitrates. |
| Alpha-blockers (e.g., terazosin, tamsulosin) | Dizziness, fainting | Your doctor may adjust your dosage or prescribe an alternative medication. |
| Some antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole) | Increased Viagra/Cialis levels in the blood | Your doctor might lower the dosage of Viagra or Cialis. |
| Ritonavir (HIV medication) | Increased Viagra/Cialis levels in the blood | Dosage adjustments are necessary. |
Grapefruit juice can also interact; avoid consuming it while taking these medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking to avoid unforeseen complications. Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial for managing your medication effectively and safely.
Which Drug is Right for You? Factors to Consider
Choose the medication that best aligns with your specific needs and health profile. Consider these key factors:
Duration of Effect
Viagra’s effects typically last 4-5 hours, while Cialis can last up to 36 hours. If you need longer-lasting relief, Cialis might be a better option. Shorter duration may suit those needing more control over timing.
Side Effects
Both medications can cause similar side effects, including headache, flushing, and nasal congestion. However, the frequency and intensity can vary between individuals. Discuss potential side effects with your doctor to determine which medication poses less risk to you personally.
Other Medications
Interactions with other medications are possible. Be completely transparent with your doctor about all medications and supplements you’re taking. This ensures a safe and effective treatment plan.
Cost
The cost of Viagra and Cialis can vary depending on your insurance coverage and pharmacy. Compare prices and explore potential cost-saving options with your physician or pharmacist.
Specific Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as heart problems or liver/kidney disease, may influence the choice of medication. Your doctor will assess your health and recommend the safest and most appropriate treatment.
Personal Preference
Ultimately, your comfort and experience with the medication are important. Discuss your preferences and concerns with your doctor. They can guide you towards a solution that fits your lifestyle and expectations.
Dosage Adjustments
Starting dosages are typically lower and adjusted according to individual response and tolerance. Your physician will tailor the dosage to achieve optimal results while minimizing potential adverse effects. Regular check-ups are vital to monitor efficacy and adjust accordingly.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Generic Viagra (sildenafil) and Cialis (tadalafil) are significantly cheaper than their brand-name counterparts. Expect to pay considerably less for generics, potentially saving you hundreds of dollars annually, depending on dosage and prescription frequency. Always check with your pharmacy for the most up-to-date pricing.
Factors Affecting Cost
- Dosage: Higher dosages generally cost more.
- Prescription Length: A three-month supply is usually cheaper per pill than a one-month supply.
- Pharmacy: Prices vary between pharmacies; online pharmacies often offer competitive pricing, but verify their legitimacy.
- Insurance Coverage: Your insurance plan may cover some or all of the cost. Check your policy details.
Accessibility is another key factor. While both medications are widely available through traditional pharmacies, online pharmacies offer a convenient alternative, especially for individuals in rural areas or those with limited mobility.
Accessing Medication
- Consult your doctor: A doctor’s prescription is necessary for both Viagra and Cialis.
- Compare pharmacy prices: Use online pharmacy comparison tools or check prices at local pharmacies.
- Explore insurance options: Determine your insurance coverage and explore potential cost-saving strategies.
- Consider online pharmacies: Choose reputable online pharmacies with verified licensing and secure payment options. Always prioritize your safety and security when purchasing medication online.
Generic vs. Brand-Name
Generic versions contain the same active ingredient as brand-name medications, but are typically much less expensive. They undergo rigorous testing to ensure bioequivalence, meaning they work the same way in the body as their brand-name counterparts.
Additional Considerations
- Potential Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects and discuss them with your physician.
- Drug Interactions: Inform your doctor of any other medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice for ED
Schedule a consultation with your doctor. This is the first and most critical step. Your doctor can accurately diagnose the underlying cause of your erectile dysfunction (ED).
Understanding Your Medical History
Be prepared to discuss your complete medical history, including any existing conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or high blood pressure. These conditions often contribute to ED. Also, mention any medications you are currently taking, as some can interfere with erectile function. Openly communicate any relevant lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, or lack of physical activity.
Diagnostic Tests
- Your doctor might order blood tests to check hormone levels and assess overall health.
- A physical examination will help rule out physical problems.
- In some cases, further testing, such as ultrasound, may be necessary.
Treatment Options
Treatment options vary widely depending on the cause and severity of ED. Your doctor will discuss the best approach for you, which may include:
- Lifestyle changes: Exercise, diet modification, and stress reduction.
- Medications: Oral medications like Viagra or Cialis, or other treatments.
- Hormone replacement therapy: If hormonal imbalances are identified.
- Penile implants or injections: In more severe cases.
- Counseling: To address psychological factors contributing to ED.
Choosing the Right Approach
Work closely with your doctor to find a treatment plan that suits your needs and preferences. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor progress and adjust the treatment as needed. Remember, finding the right solution may take time and patience.
Finding a Specialist
If your primary care physician doesn’t specialize in ED, they can refer you to a urologist or other specialist who can provide expert care. Don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion if you feel unsure about a recommended treatment.
Maintaining Open Communication
Honest and open communication with your doctor is vital for successful management of ED. Do not hesitate to ask questions or express concerns throughout the process. Early intervention and proactive management greatly improve outcomes.