Need FDA-approved Viagra? Start with a consultation with your doctor. They can assess your health, determine if Viagra (sildenafil) is right for you, and discuss potential side effects. Don’t rely on online pharmacies without a prescription; prioritize your safety.
Viagra, the brand name for sildenafil citrate, treats erectile dysfunction by increasing blood flow to the penis. The FDA approval signifies rigorous testing and confirmation of its efficacy and safety under specific conditions. Your doctor will explain these in detail.
Consider alternatives if Viagra isn’t suitable. Your physician might suggest other medications, lifestyle changes, or even counseling. Open communication is crucial for finding the best solution for your specific needs. Remember to fully discuss your medical history, including any medications you’re currently taking.
Important Note: Always obtain Viagra from a legitimate source with a valid prescription. Counterfeit medications can contain harmful ingredients. Protect your health; choose licensed pharmacies and follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously. Your doctor will provide information regarding dosage and potential interactions with other medications.
- FDA Approved Viagra: A Comprehensive Guide
- What is Viagra and How Does it Work?
- FDA Approval Process and Safety Considerations
- Understanding Potential Side Effects
- Post-Market Surveillance
- Viagra vs. Other Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
- Other Oral Medications
- Non-Oral Options
- Lifestyle Changes & Therapy
- Choosing the Right Treatment
- Obtaining a Prescription and Understanding Costs
- Long-Term Use, Potential Risks, and Alternatives
FDA Approved Viagra: A Comprehensive Guide
Consult your doctor before starting Viagra. They’ll assess your health and determine if it’s safe for you.
Viagra (sildenafil), FDA-approved in 1998, treats erectile dysfunction (ED). It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection.
Dosage: Your doctor prescribes the right dose, usually 50mg, taken as needed, one hour before sexual activity. Adjustments may be made based on your response and health conditions.
Common side effects include headaches, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and indigestion. These are usually mild and temporary. Serious side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention. Inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
Viagra is not for everyone. Men with certain heart conditions, low blood pressure, or those taking specific medications should avoid it. Don’t use Viagra if you have a history of stroke or heart attack. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Alternatives exist if Viagra isn’t suitable. Your physician can discuss other ED treatments, including Cialis, Levitra, or injections. They can also explore underlying medical conditions contributing to ED.
Storage: Store Viagra at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. Keep it out of children’s reach.
Seek professional medical advice. This information is for educational purposes only and doesn’t substitute for a doctor’s consultation. Proper diagnosis and treatment are critical for your health.
What is Viagra and How Does it Work?
Viagra (sildenafil) is a medication specifically designed to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). It achieves this by increasing blood flow to the penis.
Here’s how it works:
- Viagra inhibits an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5).
- PDE5 normally breaks down a compound called cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).
- Increased cGMP levels relax the muscles in the blood vessels of the penis.
- This relaxation allows more blood to flow into the penis, resulting in an erection.
Remember, Viagra only works when you’re sexually stimulated. It doesn’t cause erections on its own.
Before taking Viagra, consider these points:
- Consult your doctor. They’ll assess your overall health and determine if Viagra is right for you, considering any potential interactions with other medications.
- Discuss potential side effects. Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Your doctor can discuss the likelihood and severity of these based on your individual circumstances.
- Understand the dosage. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate dosage based on your needs and health profile. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
- Be aware of contraindications. Viagra is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain heart conditions, low blood pressure, or those taking specific medications should avoid Viagra.
Taking Viagra as directed by your physician can improve your sexual health. Always prioritize open communication with your doctor regarding your health and treatment.
FDA Approval Process and Safety Considerations
The FDA employs a rigorous process for drug approval, including Viagra. This involves three phases of clinical trials evaluating safety and effectiveness in increasingly larger groups. Phase 1 tests dosage and safety in a small group; Phase 2 assesses effectiveness and identifies side effects in a larger group; and Phase 3 involves thousands of participants to confirm effectiveness, monitor side effects, and compare it to existing treatments. Data from these phases is meticulously reviewed by the FDA. Approval requires demonstration of both efficacy and a favorable safety profile.
Understanding Potential Side Effects
While generally safe for most men, Viagra can cause side effects. Common ones include headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Less frequent, but serious, side effects include heart attack, stroke, and sudden hearing loss. Men with pre-existing heart conditions or high blood pressure should discuss Viagra use with their physician. This careful evaluation helps mitigate risks.
Post-Market Surveillance
FDA oversight doesn’t end with approval. Post-market surveillance continues, monitoring for long-term side effects and adverse events. Reporting any unusual reactions to your doctor and/or the FDA is crucial. This ongoing monitoring provides valuable data, contributing to a better understanding of long-term effects and potential safety issues.
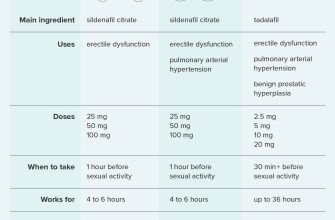
Viagra vs. Other Erectile Dysfunction Treatments
Choose the best ED treatment based on your individual needs and preferences. Viagra (sildenafil) is a popular oral medication that works by increasing blood flow to the penis. It’s generally effective, but its effects can be influenced by food and alcohol consumption. Side effects can include headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion.
Other Oral Medications
Cialis (tadalafil) offers a longer duration of action than Viagra, lasting up to 36 hours. Levitra (vardenafil) is another option with a similar mechanism of action to Viagra. Each medication has a slightly different profile regarding side effects and interactions; discuss these with your doctor.
Non-Oral Options
For men who prefer non-oral treatments, injections directly into the penis (intracavernosal injections) using medications like alprostadil offer a reliable option. Alternatively, a vacuum erection device creates a vacuum around the penis to draw blood into it, achieving an erection. Penile implants, surgically inserted, represent a more permanent solution. Each method has advantages and disadvantages in terms of effectiveness, invasiveness, and potential complications.
Lifestyle Changes & Therapy
Consider lifestyle changes alongside medication. Weight management, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction techniques can significantly improve erectile function. Psychological factors frequently contribute to ED; therapy can be beneficial in addressing underlying anxiety or relationship issues impacting sexual health. Your doctor can help determine the best course of action, considering your overall health and preferences.
Choosing the Right Treatment
Consult your doctor. They will assess your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and discuss your options to recommend the most appropriate and safe treatment for your specific circumstances. Factors like other medications you are taking and pre-existing conditions will influence the recommendation.
Obtaining a Prescription and Understanding Costs
Schedule an appointment with your doctor for a consultation. Discuss your medical history and symptoms honestly to determine if Viagra is appropriate for you.
Your doctor will conduct a physical exam and may order blood tests to assess your overall health. This is critical for safe medication use.
If Viagra is prescribed, discuss available dosage options and potential side effects. Ask questions; understanding your treatment is paramount.
The cost of Viagra varies depending on your insurance coverage, the pharmacy, and the dosage. Generic versions of sildenafil are often significantly cheaper than brand-name Viagra. Check with your insurer to see what’s covered.
Explore various pharmacy options to compare prices. Many online pharmacies offer competitive pricing, but ensure they are licensed and reputable to avoid counterfeit medications.
Consider using a prescription discount card or coupon to lower out-of-pocket expenses. Several companies offer these cards, reducing the final cost.
Be aware that the cost of Viagra may not be covered by all insurance plans. Inquire about financial assistance programs available through your pharmacy or medication manufacturer if cost is a significant barrier.
Long-Term Use, Potential Risks, and Alternatives
Consult your doctor before starting long-term Viagra use. Prolonged use might increase the risk of certain side effects, including vision changes, hearing loss, and heart problems. Regular checkups are key to monitoring your health while on the medication.
Consider potential interactions with other medications. Viagra can interact negatively with nitrates and some heart medications. Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking.
Lifestyle changes may help. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can improve erectile function naturally. Explore these options alongside or instead of medication, depending on your doctor’s advice.
Explore alternative treatments. Penile injections, vacuum erection devices, and penile implants offer alternative solutions for erectile dysfunction. Discuss these with your physician to determine suitability.
Your doctor can help you weigh the benefits and risks of long-term Viagra use against alternative treatments. They can guide you toward the best approach for your specific situation and health history.